Admin-log: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[File:Logging-syslog-2023.2.jpg|805px|frame|none]] | [[File:Logging-syslog-2023.2.jpg|805px|frame|none]] | ||
'''Number of rotated logs to keep:''' This specifies how many rotated log files will be maintained in the archive of rotated logs. | '''Number of rotated logs to keep:''' This specifies how many rotated log files will be maintained in the archive of rotated logs. | ||
'''Custom Log File Path: '''Checking this box allows you to specify a custom path for your log file. A tip is shown on this menu reminding you to make sure the path exists and is writable. (Deafult path: /var/log/messages). | |||
'''Log To Remote System: '''Checking this provide network support to the syslogd facility. Network support means that messages can be forwarded from one node running syslogd to another node running syslogd where they will be actually logged to a disk file. <ref> https://linux.die.net/man/8/syslogd </ref> | |||
'''IP Address / Port:''' In these two fields, you enter the IP address of the host machine to which syslog data will be directed, and the TCP/IP port which will be used to send that data. | '''IP Address / Port:''' In these two fields, you enter the IP address of the host machine to which syslog data will be directed, and the TCP/IP port which will be used to send that data. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 55: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
'''Connection Logging: ''' | |||
* Inbound | * Inbound | ||
Latest revision as of 20:58, 30 September 2023
Logging
The Logging Page is divided into two sections. The Syslog section contains settings to enable and configure settings for Syslog, Tomato64's main logging function. This function logs system events. The Web Monitoring section contains settings to enable and configure Tomato64's Web Monitoring function. Web Monitoring is used to monitor log/monitor web searches and which domains have been visited.
Syslog
Log Internally: This enables Tomato64's logging. By default, Tomato64 saves logs to the router's internal memory, where they may be extracted or viewed directly on the Logs page. These logs will consume router memory, but may be viewed directly on the router itself. (Default: Enabled).
Max size before rotate: Log rotation is a process that creates new log files and archives & removes old ones to save on drive space. The number entered here specifies the maximum storage space log files can occupy before they are rotated, in Kilobytes.
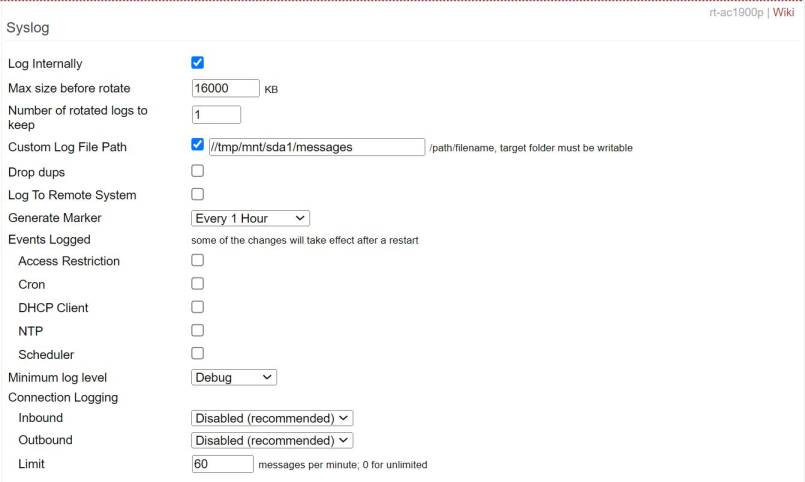
Number of rotated logs to keep: This specifies how many rotated log files will be maintained in the archive of rotated logs.
Custom Log File Path: Checking this box allows you to specify a custom path for your log file. A tip is shown on this menu reminding you to make sure the path exists and is writable. (Deafult path: /var/log/messages).
Log To Remote System: Checking this provide network support to the syslogd facility. Network support means that messages can be forwarded from one node running syslogd to another node running syslogd where they will be actually logged to a disk file. [1]
IP Address / Port: In these two fields, you enter the IP address of the host machine to which syslog data will be directed, and the TCP/IP port which will be used to send that data.
Generate Marker: This makes log files easier to read. Checking this causes the word "——MARK—–" to be inserted into the log
at the specified interval.
- Disabled
- Every 30 Minutes
- Every 1 hour
- Every 2 hours
Events Logged:
- Access Restriction - Checking this causes Access Restriction events to be logged.
- Cron - Causes Cron events to be logged.
- DHCP Client - Causes DHCP IP addressing events to be logged.
- NTP - Causes Network Time Protocol events to be logged.
- Scheduler - Causes events configured in the Tomato64 Scheduler menu to be logged.
Minimum Log Level: From this menu, you select the minimum level of messages that will be logged.
Here, "minimum" means that whichever option you select from the list, that level's messages and all those
higher in the list will be logged.
- Emergency - Only Emergency-level messages will be logged.
- Alert - Messages categorized as Alert and higher will be logged.
- Critical - Messages categorized as Critical and higher will be logged.
- Error - Messages of Error level or higher will be logged.
- Warning - Messages of Warning level or higher will be logged.
- Notice - Messages of Notice level or higher will be logged.
- Info - Messages of Information level or higher will be logged.
- Debug - Debug-level information and all other levels will be logged.
Connection Logging:
- Inbound
- Disabled - Disables logging of incoming connections.
- If Blocked by Firewall - Logs incoming connection attempts blocked by the firewall.
- If Allowed by Firewall - Logs incoming connection attempts allowed by the firewall.
- Both - Logs all incoming connection attempts.
- Outbound
- Disabled - Disables logging of outgoing connections.
- If Blocked by Firewall - Logs outgoing connection attempts blocked by the firewall.
- If Allowed by Firewall - Logs outgoing connection attempts allowed by the firewall.
- Both - Logs all outgoing connection attempts.
- Limit - Here, enter the maximum messages per minute to be logged in the system log.
Enter '0' for unlimited. (Default: 60).
Web Monitor
Clicking Enable >> Takes you to the Administration/Logging page (including Syslog settings)
Monitor Web Usage: Checking or unchecking this enables or disables Web Monitoring. (Default: Disabled)
Monitor: Select the Device/s you wish to monitor (All Computers / The following / All except). (Default: All Computers/Devices).
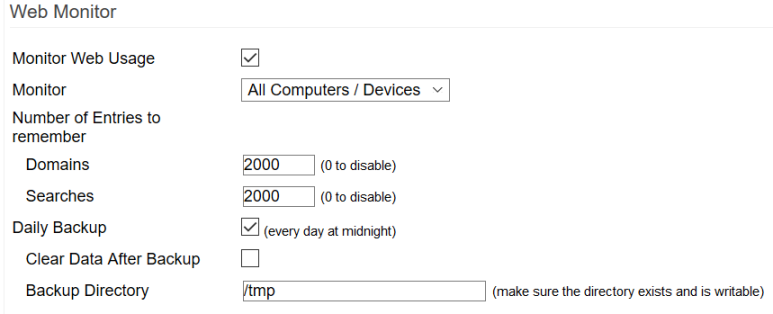
Number of Entries to remember: Here you enter the number of Domains visited and the number of Searches Tomato64 will record in the log file. Setting this to 0 makes the number of domains and searches unlimited (and therefore) allows an unlimited log size.
Daily Backup: If checked, this will enable backup of Web Monitor logs to the default backup directory. (Default: Disabled).
Clear Data After Backup: if selected, this will empty the log file after the backup is performed. (Default: Disabled)
Backup Directory: This specifies where the backup files will be stored. (Default: /tmp).
NOTE: the content of the default (\tmp) folder will be emptied ater a reboot. You might consider using USB/CIFS/JFFS storage as an alternative for more permanent storage.
Web Usage/Web Monitor Notes
Web usage will not work properly if the Tomato64 client you wish to monitor is running a direct TOR or VPN connection to the Internet. Tomato64 cannot monitor direct TOR or VPN connections because they are already encrypted.