Advanced-ctnf: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "<span id="conntrack-netfilter"></span> = Conntrack / Netfilter = The settings in this menu allow you to control some advanced network parameters. In most cases, the default settings are fine. Think very carefully before changing the settings from their defaults. You are advised to change these settings only if you have advanced networking knowledge and/or experience. <span id="connections"></span> == Connections == The Connections menu contains some limited conntrack...") |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Connections == | == Connections == | ||
The Connections menu contains some limited conntrack configuration settings. | The Connections menu contains some limited conntrack configuration settings. ''Conntrack ''is a Linux utility that provides an interface to the ''netfilter ''connection tracking system. It tracks connections, and is used to know how the packets that pass through the system are related to their connections. | ||
In general, conntrack can be used to search, list, inspect and maintain the Linux kernel's connection tracking. Conntrack does NOT manipulate packets, and works independently of NAT functions.<br /> | In general, conntrack can be used to search, list, inspect and maintain the Linux kernel's connection tracking. Conntrack does NOT manipulate packets, and works independently of NAT functions.<br /> | ||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
'''Maximum Connections''': Defines the maximum number of sessions handled by the router (<code>/proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_max</code>). | '''Maximum Connections''': Defines the maximum number of sessions handled by the router (<code>/proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_max</code>). | ||
Clicking on the [ | Clicking on the ['' Count current ... ''] link gives you a real-time view of the current demand for oconnections. | ||
'''Hash Table Size''': This parameter allows you to tweak the following kernel attribute: /<code>proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_buckets</code> | '''Hash Table Size''': This parameter allows you to tweak the following kernel attribute: /<code>proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_buckets</code> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[File: | [[File:20220110-184115.png|frame|none]] | ||
<br /> | |||
| Line 28: | Line 29: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[File: | [[File:20220110-185254.png|frame|none]] | ||
<span id="udp-timeout"></span> | <span id="udp-timeout"></span> | ||
| Line 36: | Line 37: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[File: | [[File:20220110-185419.png|frame|none]] | ||
<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 48: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[File: | [[File:20220110-185520.png|frame|none]] | ||
<span id="trackingnat-helpers"></span> | <span id="trackingnat-helpers"></span> | ||
| Line 56: | Line 58: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[File: | [[File:20220110-185610.png|frame|none]] | ||
<span id="miscellaneous"></span> | <span id="miscellaneous"></span> | ||
| Line 68: | Line 70: | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[File: | [[File:20220110-185834.png|frame|none]] | ||
<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:52, 30 September 2023
Conntrack / Netfilter
The settings in this menu allow you to control some advanced network parameters. In most cases, the default settings are fine. Think very carefully before changing the settings from their defaults. You are advised to change these settings only if you have advanced networking knowledge and/or experience.
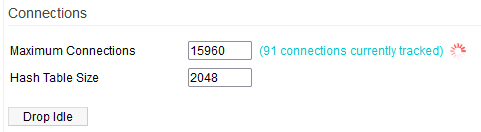
Connections
The Connections menu contains some limited conntrack configuration settings. Conntrack is a Linux utility that provides an interface to the netfilter connection tracking system. It tracks connections, and is used to know how the packets that pass through the system are related to their connections.
In general, conntrack can be used to search, list, inspect and maintain the Linux kernel's connection tracking. Conntrack does NOT manipulate packets, and works independently of NAT functions.
Maximum Connections: Defines the maximum number of sessions handled by the router (/proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_max).
Clicking on the [ Count current ... ] link gives you a real-time view of the current demand for oconnections.
Hash Table Size: This parameter allows you to tweak the following kernel attribute: /proc/sys/net/ipv4/netfilter/ip_conntrack_buckets
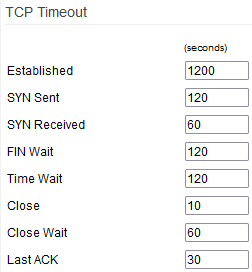
TCP Timeout
The TCP Timeout table allows you to define some critical TCP parameters, such as timeouts. These affect only connections towards the router and not through the router.
UDP Timeout
The UDP Timeout table defines the timeouts of UDP packets to and from the router.

Other Timeouts
Other Timeouts allows further adjustments to the router's timeout settings.

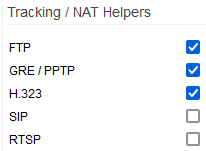
Tracking/NAT Helpers
Some protocols are well-known for being poorly designed to work with NAT. Some workarounds (Helpers) have been developed to allow these protocols to operate in a NAT environment. Enabling the option will enable the helper procedure.
Be advised that on networks where VoIP is in use, the use of the SIP helper is not recommended. While this may seem counterintuitive, real world experience shows that the SIP Helper often makes VoIP function work worse, not better.
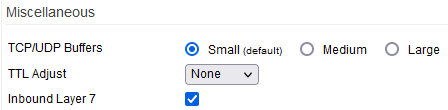
Miscellaneous
TCP/UDP Buffers: This setting defines the amount of TCP/UDP buffers allowed (to and from the router). This setting needs to be tweaked carefully. A large buffer will facilitate higher throughput, but too large a buffer might create //bufferbloat. //Bloated buffers lead to network-crippling latency spikes.
TTL Adjust: This option increases or decreases the packet Time-To-Live value crossing the router.
Inbound Layer 7: This enables Layer 7 matching for inbound traffic, caches the results, and marks the traffic as outbound.